Boris FX 9
New Features Guide
Composite Window with Integrated Keyframe Track
Key Features
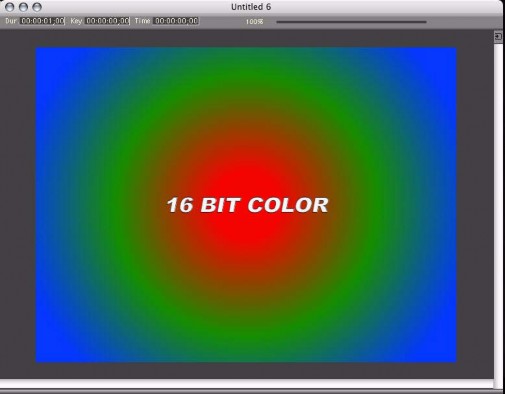
Support for 16-Bit Color
Boris software now supports 16-bit color image processing; it supports trillions of colors, which results in smoother gradients and more precise color correction.
New User Interface
This version of Boris FX incorporates NLE look and feel for smooth user interaction and transition, automatic data updates, mini Timeline in the Composite window, and popular “Sticky” and “Magnetic” windows.
New BCC Filters with Custom Preset Manager
The original filter effects in Boris FX have been replaced with the more powerful filters from the Boris Continuum Complete package, plus new filters added. The list of new filters includes blurs, particles, glows, distortions, volumetric lighting, film effects, keys and matting, and procedural generators such as snow, rain, and clouds.
New FEC Filters
Several filters from the Final Effects Complete package have been added to Boris FX, including FEC Hair, FEC Drizzle, and FEC Glass, to name a few.
Keyframe Effects Directly in the Composite Window
Now you can generate keyframed effects right within the Composite window, without the need to see the master Timelime. Select an element within the Composite window by clicking on it, and the master keyframes associated with that object appear in the mini Timeline included in the Composite window. Keyframes can be added and directly manipulated right in the mini Timeline.
New Electronic Help System
Boris FX includes a brand new fully searchable electronic Help reference system, so that you can spend more time creating effects and less time figuring out how to do it.
Image Processing
Boris software now works with both 8-bit-per-channel and 16-bit-per-channel media; 16-bit- per-channel mode makes a larger range of colors available. When you work with high- resolution images that use a narrow range of colors, such as gradients for film effects or HDTV output, 16-bit-per-channel mode means that transitions between colors display less banding, and more detail is preserved.
16-bit Image Processing
New User Interface
The Boris user interface has a new look and feel to better match your NLE editor, and includes the following improvements:
-
New Composite Window with an integrated keyframe track
-
Tab-based multi-comp Timeline window
-
Sticky windows option for easy layouts
-
Project settings and modeless options palette
-
Improved project window with a media tab
-
Configurable shortcut buttons in timeline
New Composite Window with Integrated Keyframe Track
The Composite window now contains a mini timeline where parameters can be keyframed. This allows certain effects to be animated without the aid of the timeline window, which now can be collapsed by a special button.
-
-
Sticky Windows Option
The Sticky Windows option moves windows in unison; as you resize one window, other windows resize automatically to accommodate the change. For example, when you move the Timeline up or down, the Controls and Composite windows resize as well.
Sticky Windows move in unison
Modeless Options Palette
A new Options Palette allows you to adjust many settings that were previously available in the Preferences window. This makes working with functions, such as grids and guides, an easier task. The Options Palette is a floating window; you can leave it open at all times, and the changes you make in it are instantaneous. The options palette is available for Vector Trace, Splines, Grids and Guides, Keyframe Interpolation, Keyframe Generator, and Timecode. The following example shows the Grids and Guides tab.
Configurable Shortcut Buttons in Timeline
The Timeline now includes Shortcut buttons that you can configure to suit your work style or a specific project that you are working on. You can rearrange the buttons to your liking by selecting and dragging them.
New Filters
Boris FX now includes brand new filters from the most recent Boris Continuum Complete (BCC) and Final Effect Complete (FEC) releases. These powerful new filters are a significant addition to the product and ease the work of such common tasks as foreground object removal and image stabilization.
Color and Blurs Filters
BCC Artist’s Poster
Artist’s Poster creates a posterized effect by reducing the image to eight “pure” colors (Red, Green, Blue, Cyan, Magenta, Yellow, Black, and White) and processing each color separately. At its default settings the filter outputs the NTSC-safe color that is closest to each of these eight colors.
Source image Filtered image
BCC Blur
Blur emulates the look of shooting in soft focus or with lens diffusion. This filter allows you to blur the horizontal and vertical components of the image independently.
If the source image is opaque, selecting the Opaque Source checkbox can speed rendering and preview times. If your source is partially transparent, deselect this option for best results.
Horizontal Blur and Vertical Blur control the amount of blur in each direction. Increasing these values increases the amount of blur that is applied to the image. If the Lock Blur checkbox is checked, Horizontal Blur sets the blur amount in both directions.
Source image Horizontal Blur=60 Vertical Blur=60
BCC Boost Blend
Boost Blend is a compositing filter that blends two independent layers in a composition and adjusts contrast in the blended pixels. Unlike most transfer modes, Boost Blend adjusts the mix only where the source and blend layers are different. Boost Blend is especially useful when you composite an image over itself and do not want the Apply mode to affect areas where the blended pixels are identical to the source pixels. The PixelChooser provides additional control over the selection of pixels to adjust.
The Blend Layer menu chooses any clip or layer to blend with the source layer (the clip or layer to which Boost Blend is applied). The illustrations below show the source layer and the blend layer used in the examples in this section.
Source layer Blend layer
BCC Brightness-Contrast
Brightness-Contrast adjusts the brightness and contrast in your image. This filter also has a PixelChooser, so you can select which pixels to adjust.
Brightness adjusts the brightness of the image. Increasing the Brightness setting pushes colors toward white, and decreasing the setting pushes colors toward black.
Brightness=–40 Brightness=0 Brightness=40
BCC Color Balance
Color Balance performs a true photographic RGB color correction, allowing you to make independent adjustments to the red, green, and blue channels of the image.
BCC Color Choker Filter
This filter independently chokes the red, green, and blue channels of an image. It is intended for use with opaque images and does not use the alpha channel. The controls are very similar to those in the Composite Choker filter, except that the latter filter affects alpha. Use this filter to create effects in which color details have more contrast and are softer. In the default choke mode.
Source Image Color Blowout preset applied EvenDifference preset applied
Red Choke 1=–13 Red Choke 1=–2 Red Choke 1=15
BCC Color Correction
The Color Correction filter improves the color of images or creates dramatic color effects. Allows you to adjust Brightness, Contrast, Hue, Saturation, luminance level of Blacl pixels, and luminence level of White pixels.
Hue= –20 Hue=0 Hue=20
Saturation= –20 Saturation=0 Saturation=20
BCC Color Match
BCC Color Match simplifies the process of matching the color or luma values of two clips in the timeline. For instance, if two clips with different lighting conditions are spliced together, the clips color and luma values will differ. Match Color automates the process of removing or balancing the difference between the two clips by setting color or luma values for the highlight, mid, and shadow areas of the image.
Original image Filtered image (and matched target clip)
BCC Color Palette
The Color Palette filter provides a number of ways to select colors from the host user interface for your project. You can also use the Color Palette filter to set colors which can be used any number of times within the current project.
BCC Colorize
Colorize uses a gradient of up to six colors to tone the image. All of the parameters in this filter can be animated and linked to other parameters.
Source image Filtered image
BCC Correct Selected Color
This filter allows you to adjust a specified range of colors in the source image, leaving colors outside the range unaffected.
Source image Filtered image
BCC Directional Blur
Directional Blur blurs the image by displacing it in one direction. The effect is similar to how a photograph of a speeding object appears if taken with a slower shutter speed.
Source image Filtered image
BCC Gaussian Blur
The Gaussian Blur filter implements a popular blur algorithm that produces smoother blurs but takes more time to render than the Basic Blur filter. Gaussian Blur softens the image by averaging each pixel with its neighboring pixels. The word “Gaussian” refers to the bell- shaped curve commonly used in statistical analysis. The shape of this curve determines how much each averaged pixel contributes to the output.
Source image Filtered image
BCC Hue-Saturation-Lightness
Hue-Saturation-Lightness converts the image to the Hue/Saturation/Lightness color space, makes corrections to the image, and converts it back to RGB.
BCC Invert Solarize
Invert Solarize inverts one or more channels in the source image.
Source image Filtered image
BCC Levels Gamma
Levels Gamma provides options for adjusting contrast and eliminating noise in your image. Video shot at night or in poorly lit settings often contains noise in the dark areas. Increasing Input Black removes this noise by treating all areas darker than the Input Black setting as black. Washed out or overexposed images do not contain the full range of levels. Increasing Input Black and/or decreasing Input White can boost the contrast of the image.
Input Black=0 Input Black=75 Input Black=125
BCC Motion Blur Filter
The BCC Motion Blur filter creates a realistic blur on the motion in an image, simulating the effect of shooting a moving object on film. The blur is based on the motion of the pixels in the image. For example, you could apply the Motion Blur filter to a clip of a speeding car and thecar’s motion would blur while the background would not. The blur is most pronounced when the object moves quickly and more subtle when it moves slowly. Motion blur is not visible if the image is static.
-
Source image Source image Filtered image
BCC MultiTone Mix
The MultiTone Mix filter uses the source image’s color, luma, or alpha information to create a toned image that uses up to five independent colors. MultiTone Mix works by creating a color map based on a specific channel in the source image, then replacing each color range in the map with a new color.
Source image Filtered image
BCC Posterize
Posterize reduces the number of colors in the image by independently reducing the number of discrete levels in each color channel. The resulting output image has a few distinct values of red, green, and blue, instead of having each value spread over the full range of 0 to 255. The filter also allows you to scramble the output values for additional creative control.
Posterization effects can produce hard edges that give the output image a rough appearance, which can be exacerbated by image compression and by the bandwidth limitations of analog video equipment. The Posterize filter provides several controls that deal with such problems by blurring and softening the posterized image.
RGB Levels=2 RGB Levels=3 RGB Levels=5
BCC Pyramid Blur Filter
The BCC Pyramid Blur filter emulates the look of shooting in soft focus or with lens diffusion. This filter allows you to blur the horizontal and vertical components of the image separately. The functionality is similar to the BCC Blur filter. However, BCC Pyramid Blur uses a refined algorithm that speeds rendering approximately 20 - 40 percent. When you create new blur effects, you should use this filter.
Original Image Filtered Image
BCC Radial Blur Filter
The BCC Radial Blur filter creates a blur around a specific point, simulating the affect of a zooming or rotating camera. The Amount option specifies the amount of blur, depending on the selection for Type. For a Spin blur, which applies blurs in circles around the center point, the Amount value indicates the degree of rotation. For a Zoom blur, which applies blur that radiates out from the center point, the Amount value specifies the degree of radial blurring.
Original Image Filtered Image
BCC Safe Colors Filter
The BCC Safe Colors filter prevents clips from having saturation values that exceed the legal limits of broadcast standards. Use this filter to limit the values that are present in the image.
BCC Spiral Blur Filter
The BCC Spiral Blur filter creates a blur or smear that appears as though it is spiraling toward the center of the image.
Original Image Filtered Image
BCC Tritone
Tritone creates a toned image from the source image’s luma channel or any of its RGB channels. The Input Channel maps to a color range that goes from the Black Color to the Middle Color to the White Color. The default Tritone uses the source’s luma channel as the Input Channel to produce an image that is black where the source is black, white where the source is white, and blue-toned in the gray regions.
Source image Filtered image
BCC Unsharp Mask
The Unsharp Mask filter uses a classic image sharpening technique similar to the method used to sharpen film images. The source image is blurred, and the blurred image is then subtracted from the source. The resulting image is sharper and has more contrast. Unsharp
Mask sharpens areas in an image with significant color changes by adjusting the contrast of edge details to create the illusion of image sharpness. This filter is useful for refocusing an image that appears blurry due to scanning, poor lighting, or other factors.
Source image Filtered image
Distortion & Perspective Filters
BCC 2D Particles and 2D Particles Advanced
2D Particles breaks the source image into particles and disperses them in 2D space. This filter also provides a variety of explosion, velocity, and gravity controls to adjust the particles movement. You can also control the size, shape, density, and opacity of the particles, and create custom particle shapes and scatter wipes. Use the auto-animation feature to easily generate explosion effects, or animate the filter manually for precise control.
Source image Filtered image
BCC 3D Image Shatter
3D Image Shatter shatters the image in 3D space and disperses the image fragments. The filter provides a variety of explosion, velocity, and gravity parameters to control particle movement. In addition, 3D Image Shatter has a number of parameters that allow you to
control the particle size and shape, rotation, opacity, lighting, and explosion style. This filter is auto-animated by default, but you can manually animate it for more precise control over the movement and dispersion of the particles.
3D Image Shatter effect
Time 00:00:00:00 Time 00:00:00:15 Time 00:00:01:00
BCC Bulge
Bulge makes the source image appear as if it is stretched over a surface with a bulge or a depression.
Height=50 Height=–50
BCC Corner Pin
The BCC Corner Pin filter allows you to map media to a specific area on a moving object in a media file. For example, suppose your movie includes a moving bus with an advertisement on its side. You could use Corner Pin to track and replace the advertisement with a logo.
Original image Corner Pin Image Filtered image
BCC Displacement Map
The Displacement Map filter uses the luminance or color information from an alternate video or still image track (the Map Layer) to displace the pixels in the source image horizontally and vertically. This filter creates a distorted version of the source whose distorted regions correspond to the luma or color channel of the Map Layer’s media.
Source image Map Layer Filtered image
BCC Edge Bevel
Edge Bevel creates the appearance of a beveled edge around the borders of an image. To create an Edge Bevel effect, select a track and choose Filters > Distortion and Perspective > Edge Bevel.
Source Image Filtered image
BCC Fast Flipper
Fast Flipper flips or mirrors your image. You can flip your image vertically or horizontally, or define an invisible mirror line that mirrors your image in various directions. You can also blend the mirror line to produce a smoother transition between the original and mirrored images. Resampling is on a pixel-for-pixel basis, so the filter is fast and no quality is lost.
Source image Filtered image (flipped horizontally)
BCC Polar Displacement
The Polar Displacement filter uses a Map Layer to displace pixels radially outward from the Center Point and angularly along an arc of a circle centered at the Center Point.
Source image Map Layer Filtered image
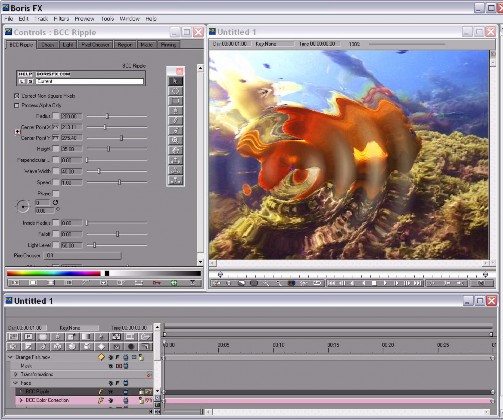
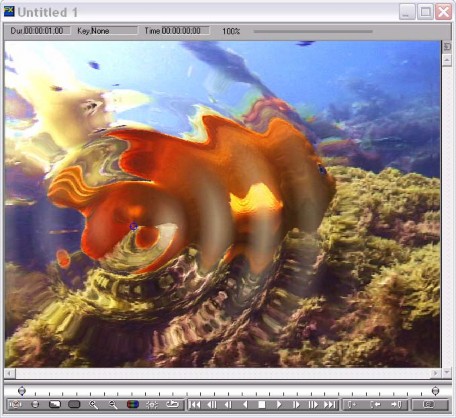
BCC Ripple
The Ripple filter simulates ripples spreading out from a point of origin in a pool of water, similar to what you see after tossing a pebble into a pond. This filter automatically creates animated ripples and allows you to choose from a range of wave shapes.
Source image Filtered image
BCC Turbulence Filter
The turbulence filter is a Noise Map 2 filter wired to a displacement map. All of the controls that affect distortion are identical to those in the BCC Displacement Map filter. All of the other controls are identical to those in the Noise Map 2 filter. There is one additional control, View Texture, which views the Noise Map and produces the same output as a Noise Map 2 filter with the same controls.
Original Image Spooky Noise preset applied Ring and Scale preset applied
BCC Twirl
The BCC Twirl filter spins the image around a center point, creating a spiral of distortion.
Source image Filtered image
BCC Vector Displacement
Vector Displacement uses the RGB channels in the Map Layer to displace the image in three different directions.
BCC Wave
The Wave and Ripple filters are very similar, except that Wave creates parallel waves instead of waves that radiate from a point.
Source image Filtered image
Effects Filters
BCC Alpha Pixel Noise
Alpha Pixel Noise adds noise to an image’s alpha channel. You can use this filter to create pixelated transitions between two images.
Alpha Pixel Noise transition
Time 00:00:01:00 Time 00:00:02:00 Time 00:00:03:00
BCC Alpha Spotlight
Alpha Spotlight uses a spotlight to create or add transparency to the source image. For example, you can use Alpha Spotlight to create an effect in which the lit areas become transparent while the background is left opaque, or vice versa.
Source image Filtered image
BCC Burnt Film
Burnt Film simulates the look of holes burning through a layer of film to reveal another image. This filter provides control over the appearance of the burned edges and the burn rate, and allows you to use a custom alpha matte to set the shape of the burn holes.
Burnt Film transition
Time 00:00:01:00 Time 00:00:02:00
BCC Cartooner
The Cartooner filter allows you to draw an outline around the edges in one of an image’s color or alpha channels. You can also use the Cartooner filter to turn a video source into an outline animation.
The filter compares a selected channel in the source with a threshold value to create an edge map. Cartooner then blurs the map and strokes the edges in the map.
The results obtained with the edge filters vary depending on the media to which the filter is applied and the exact settings used. Because they create edge effects by emphasizing differences between adjacent pixels, edge filters are very sensitive to parameter adjustments. Often a very small change in a parameter can dramatically affect the result.
Edge Source Layer Filtered image
BCC Colorize Glow
The Colorize Glow filter is similar to the Glow filter but it generates the glow from a single channel and then applies a gradient to the glow. The Colorized Glow can be composited with the original image or viewed by itself.
Source image Filtered image
BCC Deinterlace Filter
The BCC Deinterlace filter converts interlaced video clips into progressive-scan frames, such as footage shot on film. Deinterlace can render “simulated TeleCine” style by adding pulldown. This filter can also convert 29.97fps NTSC video into 24fps film-style frames.
BCC DeNoise
The BCC DeNoise filter removes unwanted pixel noise from an image. DeNoise is especially useful when working with archival materials, as it lets you correct dark areas that show artifacts from film emulsion or video compression. You may also want to use the BCC DeNoise filter when resizing 4:3 images to 16:9 aspect ratio.
The BCC DeNoise filter distinguishes between moving areas and areas that are static. This allows the filter to selectively remove noise only from static areas. This preserves the full detail of areas that are in motion.
DeNoise uses temporal and spacial smoothing to eliminate the artifacts, based on alternate frames in the video. Since the smoothing algorithm is based on a sequence of frames, it is difficult to show the effects of this filter in a still image.
BCC Drop Shadow Filter
The BCC Drop Shadow filter allows you to apply an animatable drop shadow to titles or clips in the timeline.
Source image Filtered image
BCC Dust and Scratches
The BCC Dust and Scratches filter removes unwanted dust and scratches from an image. The PixelChooser is especially useful to specify which areas the filter should affect.
Original Image Filtered Image
BCC Emboss
Emboss simulates the appearance of an embossed or raised image by converting the source to a solid color and lighting the edges in the source’s luma channel.
Source image Filtered image
BCC Glow
The Glow filter uses a blur to create a glowing effect, highlighting the edges in the chosen channel. This filter is different from the Glow filter included in earlier versions of BCC; that filter has been renamed BCC Rough Glow. If you are creating a new effect, you should use the BCC Glow filter.
The Glow finds the brighter parts of an image and then brightens those and surrounding pixels to create a diffuse, glowing halo. The Glow can also simulate overexposure of brightly lit objects. You can base the glow on either the original colors of the image or on a chosen channel. You can also use the Glow to create a gradient glow between two colors and to create multicolor effects with looping.
Source image Filtered image
BCC Glow Alpha Edges Filter
The BCC Glow Alpha Edges filter applies a glow that adheres to the contours of the image’s alpha channel or mask. Use this filter with masks or images that have an alpha channel.
Original Image Filtered Image
BCC Halftone Filter
The BCC Halftone filter simulates the look of printed material by converting the image to simulated halftone dots. Print images are comprised of a rosette pattern of colored ink dots. To avoid moiré or interference patterns, the dots are printed at different angles; this process is known as halftone screening. This is also used in the art world as a creative process such as the work produced by Lichtenstein.
Original image Filtered image
BCC Median Filter
The BCC Median filter makes each pixel look like the majority of its neighboring pixels. It produces a smeary look, but with sharp edges (at neighborhood boundaries). The Median filter also reduces noise by eliminating “spikes”, or pixels that are very different from their neighbors (also referred to as “salt and pepper noise”).
Original image Filtered image
BCC Misalignment Filter
The BCC Misalignment filter simulates the effect of misaligned RGB color channels.
Unfiltered Image Filtered Image
BCC Mosaic
Mosaic allows you to pixelate images to achieve a range of mosaic effects using a few simple parameters and a PixelChooser.
Source image Filtered image
BCC Multi Shadow
Multi Shadow is a versatile filter which you can use to composite three or more independent drop shadows over a source image.
Source image Filtered image
BCC RGB Edges
RGB Edges finds edges in each RGB channel independently, creates a new RGB image from these edges, and applies the new image to the source using the chosen Apply Mode and Apply Mix.
The results obtained with the edge filters vary depending on the media to which the filter is applied and the exact settings used. Because they create edge effects by emphasizing differences between adjacent pixels, edge filters are very sensitive to parameter adjustments. Often a small change in a parameter setting can dramatically affect the result.
Source image Filtered image
BCC RGB Pixel Noise
RGB Pixel noise applies noise to each of the RGB color channels independently. Alternately, you can use this filter to apply noise to the source image’s luminance channel without changing the pixels’ colors.
Source image Filtered image
BCC Rough Glow
The Rough Glow filter uses a blur to create a glowing effect, highlighting the edges in the image. In earlier versions of BCC, this filter was named BCC Glow. If you are creating a new effect, you should use the BCC Glow filter. This filter is included to provide compatibility with older settings.
Source image Filtered image
BCC Scatterize
Scatterize shuffles the pixels in the source image, creating a scattered effect.
Variance determines how scattered the image is and works in conjunction with the Scatter Percentage parameter.
Variance=0 Variance=10 Variance=30
BCC Spray Paint Noise
Spray Paint Noise applies a flat spray paint color to the image.
Source image Filtered image
BCC Witness Protection Filter
The Witness Protection filter allows you to track the motion of an object in a media file. You can then use the motion track data to control another aspect of the effect. For example, track a logo on a t-shirt and use a blur to obscure it. You can apply a mosaic, blur, tint or brightness/contrast effect to the specified area.
Unfiltered Image Filtered Image
FEC Plug-Ins
FEC Blobbylize Filter
FEC Blobbylize w/Blob Map uses gradient map defined by another input to create a blobby, glossy cutout of the other image. The Blob Layer can be virtually anything, from simple text to a complex particle animation.
Unfiltered Image Filtered Image
FEC Drizzle Filter
FEC Drizzle is a particle-based simulation of circular ripples on a watery surface akin to ripples on a pond caused by light raindrops.
Unfiltered Image Filtered Image
FEC Glass Filter
FEC Glass creates a convincing glass-like appearance. To accomplish this effect, the selected image defines a bump map, which is then used to create a glossy, 3D texture. Use FEC Glass to create dramatic and innovative effects by using values from a different layer to create the illusion of that layer rising through the source layer.
Unfiltered Image Filtered Image
FEC Hair Filter
FEC Hair creates particles that stretch into filaments like hair. Hair uses a chosen property to determine where hair should grow.
Unfiltered Image Filtered Image
FEC Kaleida Filter
The FEC Kaleida filter creates a kaleidoscopic effect on the source image. The kaleidoscope image becomes a tile that is repeated across the image.
Source Image CrazyDaisy2 preset applied Stars Expand Right preset applied
Generators Filters
BCC Caustics
The BCC Caustics filter can be used to simulate the effect of light refracting through a surface of water and projected onto a surface (like moving water ripple reflections on a pool bottom). You can use this filter to create many types of effects where rays emanate from a point and are reflected or refracted by a curved surface. For example, you could use this filter to generate moving plasma fields, smoky particle effects, waves in a pool, or animating geometric patterns.
smoky effect pool effect
BCC Fractal Noise
Fractal Noise creates a simulated marble texture.
BCC Noise Map
Noise Map is a procedural noise generator that produces a continuously flowing gradient that can be used to provide organic input to other filters. Because the noise is continuous, there is never a seam.
Noise Map 2
The Noise Map 2 filter uses a three dimensional noise map to generate monochrome textures for use as backgrounds, mattes, or alternate sources to control other filters. The filter generates multiple layers of noise and superimposes them to produce the output texture.
Layer Thin Strands preset Noisy Strings preset Wave Hypno Zoom preset
BCC Rays
The BCC Rays Generator creates a ray burst effect. The rays can act as a filter on a clip or layer or generate a ray layer. The Rays effect is comprised of two discrete elements, the rays and the glow. The filter provides controls for adjusting each element individually. The rays can be composited over the source image, or you can generate a completely synthetic image.
Rays Rays with Glow
Lights Filters
BCC Rays Cartoon Filter
The BCC Rays Cartoon filter creates the light out of the Cartoon edges of the filter. Using it is the same as using one of the other Rays filters with the Light From channel set to one of the Cartoon Edges choices.
Unfiltered Image Filtered Image
BCC Rays Puffy Filter
The BCC Rays Puffy filter light which spreads from a source point creating a soft, “puffy” appearance. The light is generated from a chosen channel in the source image.
Unfiltered Image Filtered Image
BCC Rays Radiant Edges Filter
The BCC Rays Radiant Edges filter creates light from the edges of the image. This filter includes similar controls to the BCC Rays Cartoon filter.
Unfiltered Image Filtered Image
BCC Rays Radiant Spotlight Filter
The BCC Rays Radiant Spotlight filter is a combination of a Light Ray Filter and a Spotlight. The spotlight can be used to matte either the light source or the rendered light.
Unfiltered Image Filtered Image
BCC Rays Ring Filter
The BCC Rays Ring filter masks the light source with a ring. The resulting light is generated from a selected channel in the source image and spreads from a source point in all directions.
Unfiltered Image Filtered Image
BCC Rays Ripply Filter
The BCC Rays Ripply filter combines a light rays effect with a rippled light effect. The resulting light is generated from a chosen channel in the source image and spreads from a source point in all directions.
Unfiltered Image Filtered Image
BCC Rays Streaky Filter
The BCC Rays Streaky filter produces a light that contains streaks. The resulting light is generated from a chosen channel in the source image, and spreads from a source point in all directions.
Unfiltered Image Filtered Image
BCC Rays Textured Filter
The BCC Rays Textured filter creates a textured light using a noise map pattern. The resulting light is generated from a chosen channel in the source image, and spreads from a source point in all directions.
Unfiltered Image Filtered Image
BCC Rays Wedge Filter
The BCC Rays Wedge filter is a light rays filter that mattes the light source with a wedge- shaped light. The resulting light is generated from a selected channel in the source image, and spreads from a source point in all directions.
Unfiltered Image Filtered Image
Motion Filters
Corner Pin Tracker
The Corner Pin Tracker allows you to map media to a specific area on a moving object in a media file. For example, suppose your movie includes a moving bus with an advertisement on its side. You could use Corner Pin Tracker to replace the advertisement with a logo.
Motion Tracker
The Motion Tracker filter allows you to generate motion path data by estimating the motion of an object in a media file. You can then use this data to control the motion of another aspect of the effect. For example, use the Motion Tracker to create an effect in which text or a spline object follows a moving object in a media file. You can also use Tracker data with filters,
allowing you to cause applied lights, blurs or other filters to follow an object.
New Library Browser Presets
New Library Browser Presets
Boris FX includes over 70 new professionally designed Library Browser Presets in the following categories:
-
New additions
-
New Lower Thirds
-
New Presets/Steve Oakley: Film FX Filters, Transitions, & Wedding
New Host Support
Boris products add support for Avid AVX 2.0 API on Windows, enabling the application to take advantage of 16-bit color processing and Avid’s advanced key framing model. Support for Sony Vegas 7.0, Canopus Edius 4.0, and Harris Velocity is also new in this release, including support for the Media Generator in Sony Vegas. Later this year, support will be added for the Avid AVX 2.0 API on Macintosh systems.
Boris products supports the following host applications:
Macintosh Windows
Boris Engine or Keyframer Boris Engine or Keyframer
Apple® Final Cut Pro HD® 5.0 or later Adobe® Premiere Pro® 1.5 and 2.0
Avid AVX 1.5 API:
Avid® Media Composer® 11.7 and later Avid® Media Composer® Adrenaline 2.5 Avid Symphony® 4.5 and later
Avid XpressMac®
Avid Xpress DV® 4.8 and later Avid Xpress Pro® 4.0 or later
Avid AVX 1.0 API:
Avid|DS 6.0 through 7.6 Avid AVX 1.5 API:
Avid® Media Composer® Avid Symphony®
Avid Xpress®,
Avid Xpress DV® 3.0, 3.5.4 Avid Xpress Pro® 4.0 or later Avid Xpress Studio
Avid Liquid® 7.0 Avid AVX 2.0 API:
Avid Xpress Pro® 5.5 or later
Media Composer 2.5 or later Avid Symphony Nitris 1.5.x Avid Symphony 3.5 and later
Avid Adrenaline Newscutter 6.5.x
Canopus® Edius 3.x and 4.0
Harris Velocity X
Media 100 i® 8.1 or later Media 100 HD 10.x Media 100 sw
Sony® Vegas® 5.0 and later
Supported Operating Systems
Boris products supports the following operating systems:
-
Microsoft® Windows® and Windows XP® SP2
-
Apple Macintosh OS 10.4.X
System Requirements
-
A minimum 1 GB of RAM is required, and 2 GB is recommended when using Boris software with a host application.
-
512 MB of memory is required when using Boris software standalone.
-
QuickTime version 6.5 or later installed